By Admin – Steroidal.com
Hay fever affects a large part of various countries and is also one of the hardest conditions to control. Hay fever is also called allergic rhinitis and arises from pollen inhalation, but the same effects can be experienced from dust and insect venoms. A seasonal condition, the symptoms are; sneezing, itchy or painful nose, face, eyes and runny or blocked nose. Other symptoms are fatigue and lethargy.
Anyone that’s had bad hay fever will know it’s not fun but hard to avoid. Actually, as I write this article, I’m experiencing it and have done for the last three weeks!
Hay fever is an immune reaction to foreign particles it can’t account for. Your immune system mistakes pollen proteins for bacteria, virus’s or other dangerous intruders and must excrete them at all costs. Your immune system is sensitised during certain times of the year and those with hyper sensitised immune systems experience the worst incidences of hay fever.
We know that fish oil, or omega-3, is a pretty potent anti-inflammatory, so in theory that alone should reduce hay fever occurring. Consuming a diet high in omega-3 would mean more being present in your cell membranes and blood and that’s important. So what can fish oil do for hay fever?
We’re going to look at a study done in 2005, by nutritionists at the Technical University of Munich who looked at precisely this [1].
The German researchers measured the amount of omega-3 fatty acids present in the membranes of the red blood cells of 325 women and 243 men (568). Firstly, the scientists wanted to know which of whom of their subjects was sensitised to hay fever, so they looked to see if any of them had anti-bodies against pollen proteins. They then asked the subjects if they were troubles by hay fever at all.
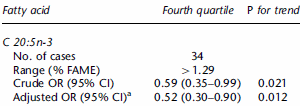
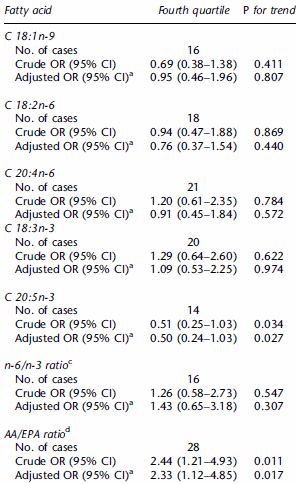
What they found was the more eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) the subjects had in their blood, the less often their immune systems were sensitised to hay fever.
The researchers then set the chance of sensitisation of the 25% of the subjects with the lowest EPA in their blood at 1. The 25% of the test subjects with the most EPA in their blood was half.
When the Germans looked at the chance of the subjects having hay fever, the relationship was the same.
A possible explanation is the arachidonic acid [AA] and the EPA ratio. AA is a metabolite of omega-6, which is precursor of various inflammatory factors. The ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 is important it seems here again. Low vegetable oil intake, processed foods and high omega-3 intake, obtaining a balance in both would help reduce the chances of hay fever or its severity.
That said, we did also find a 1993 older and perhaps out-dated study, that claimed omega-3 intake does nothing for allergic rhinitis [2]. The study concluded, “We conclude that dietary fish oil supplementation does not prevent seasonal hay fever and asthma in pollen-sensitive subjects during the pollen season.”
We’d suggest elevating fish oil intake, not only due to it possible helping hay fever, but due to its many benefits. Increasing muscle building, clearing acne and lowering blood pressure and cholesterol are just some of its many positives, and if its not part of your daily diet or supplementation program – it should be.
References:
[1]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2005) 59, 1071–1080.
[2]. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 May;147(5):1138-43.