By Anthoney J. Andersen – Steroidal.com
Whether you’re a bodybuilder or a fitness enthusiast, pushing your body to new heights will eventually become a key component to your workout regimen. Not only will you be searching for new exercises to incorporate into your weekly routine, but you will be searching for new ways to increase your body’s lean muscle mass.
If you’re finding that your body has hit a bit of a ‘road block,’ and you can’t quite seem to get your body’s lean muscle/fat percentage to a place of personal gratification, then the following amino acid should be an essential part of your daily diet.
The amino acid in question is called L-leucine.
L-leucine is an essential amino acid, meaning you must obtain it through diet because your body cannot produce it. You can acquire leucine by eating meat, dairy products, eggs, soy and other beans – or by taking it as a supplement.
According to Livestrong.com, leucine has potential benefits for weight loss, lean muscle mass and cholesterol levels.
MUSCLE PRESERVATION
Leucine, like other essential amino acids, helps maintain muscle mass. For this reason, many bodybuilders and athletes take leucine supplements. In the December 1, 2005 issue of the “Journal of Physiology,” one study with animals found that feeding aged rats leucine inhibited muscle protein breakdown.
Another article in the journal discusses this research, explaining that although decreasing dietary fat is advisable for older people, continuing eating high quality protein is important.
Leucine works with the amino acids isoleucine and valine to repair muscles, regulate blood sugar and provide the body with energy. It also increases production of growth hormones, and helps burn visceral fat – which is in the deepest layers of the body and the least responsive to dieting and exercise.
Leucine, isoleucine and valine are branched chain amino acids (BCAAs), and all three of them help promote muscle recovery after exercise. Leucine is the most effective BCAA for preventing muscle loss because it breaks down and is converted to glucose more quickly than isoleucine and valine.
Increased glucose prevents the body’s ‘cannibalization of muscle’ for energy during intense workouts, which proves why this amino acid is so popular among professional bodybuilders.
THE PROCESS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
You have probably heard the term ‘protein synthesis’ being used when reading articles about muscle growth.
But what is it, exactly?
The simplest explanation is that protein synthesis is the fusion of new skeletal muscle proteins.
Protein synthesis is one of the most fundamental biological processes by which individual cells build their specific proteins. Involved in the process of protein synthesis is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, the process is initiated in the cell’s nucleus, where specific enzymes unwind the needed section of DNA, which makes the DNA in this region accessible and a RNA copy can be created. This RNA molecule then moves from the nucleus to the cell cytoplasm, where the actual process of protein synthesis takes place.
Exercise has a profound effect on muscle growth, which can only occur if muscle protein synthesis exceeds muscle protein breakdown (there must be a positive muscle protein balance involved). Resistance exercise improves muscle protein balance, but in the absence of food intake, the balance remains negative (i.e. catabolic).
The response of muscle protein metabolism to resistance exercise lasts for roughly 24 to 48 hours; thus, the interaction between protein metabolism and any meals consumed in this period will determine the impact of the diet on muscle hypertrophy – referred to as the increase in muscle size due to the enlargement of the size of the cells, as opposed to an increase in the number of cells – known as hyperplasia.
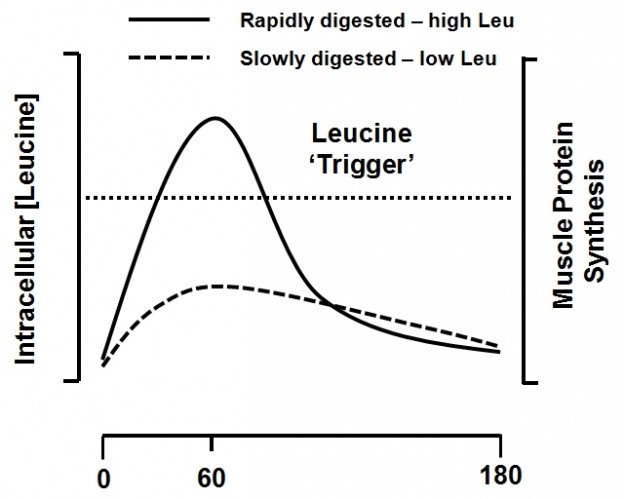
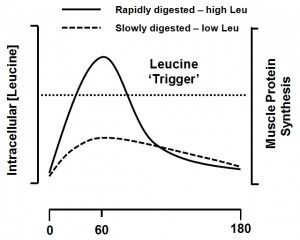
LEUCINE STIMULATES PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TO BUILD MUSCLE
Whether you’re interested in building muscle or preventing muscle loss that occurs during dieting and aging, stimulating protein synthesis is absolutely imperative. Most people know that consuming protein creates an increase in muscle protein synthesis, which is why protein supplements are popular to consume after exercise.
According to Nutritionexpress.com, researchers are beginning to refine their knowledge on why protein stimulates anabolism (building up) in muscle. Scientists have discovered that it is the level of amino acids in the blood that directly boosts protein synthesis in muscles.
In particular, scientists have found that leucine is most highly related to protein synthesis. In a series of elaborate experiments, researchers directly examined muscle protein synthesis after feeding animals various formulations of amino acids, while comparing them to glucose ingestion. When a complete protein (one that contains all the amino acids) was consumed, protein synthesis increased. However, when just essential amino acids were consumed without non-essential amino acids, the same increase was noted, indicating that non-essential amino acids are not required to stimulate protein synthesis.
Finally, when just leucine was consumed, protein synthesis still increased to the same magnitude. These findings provided strong evidence that leucine was the driving force behind the ability of dietary protein to stimulate protein synthesis.
According to Naturalnews.com, the latest science has proven that a special protein called mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) holds the key to muscle building and rejuvenation. When mTOR is activated, is causes muscle cells to increase protein synthesis. This leads to skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
mTOR integrates cellular information regarding intracellular nutrient status and energy, and oxidative stress levels. When mTOR deems that the energy levels are high and the muscle cells are stressed, it activates in order to help the cells heal and rebuild in a stronger manner.
The most effective ways to regulate mTOR activity is through fasting (which reduces the body’s need for insulin signaling), high intensity exercise and the intake of BCAAs. All of these actions help to improve cellular insulin sensitivity, as does eating an anti-inflammatory diet that is rich in phytonutrient rich fruits and vegetables, healthy fats and grass-fed animal products.
CONCLUSION
As research has discovered, leucine consumption can provide multiple benefits for the body. It provides an important building block for muscle protein, activates key components in the complex process of protein synthesis, contributes to weight loss, improves body composition and corrects metabolic disturbances, such as elevated glucose and cholesterol levels.
The ideal amount of leucine is still up for debate. However, when single doses have been studied, an intake of as little as 2.5 grams of leucine was found to have stimulated protein synthesis. In long-term studies, leucine intakes of eight or more grams per day are recommended in divided doses, so that the 2.5 grams of leucine are consumed at each meal.